十一、手写防抖节流和深拷贝和事件总线工具函数
Lyk 2022/8/12 ES6防抖节流深拷贝事件总线
# 1、防抖debounce函数的深入学习
# 1.1.认识防抖和节流函数
- 防抖和节流的概念其实最早并不是出现在软件工程中,防抖是出现在电子元件中,节流出现在流体流动中
- 而JavaScript是事件驱动的,大量的操作会触发事件,加入到事件队列中处理。
- 而对于某些频繁的事件处理会造成性能的损耗,我们就可以通过防抖和节流来限制事件频繁的发生;
- 防抖和节流函数目前已经是前端实际开发中两个非常重要的函数,也是面试经常被问到的面试题。
- 但是很多前端开发者面对这两个功能,有点摸不着头脑:
- 某些开发者根本无法区分防抖和节流有什么区别(面试经常会被问到);
- 某些开发者可以区分,但是不知道如何应用;
- 某些开发者会通过一些第三方库(
Underscore的官网(opens new window))来使用,但是不知道内部原理,更不会编写;
- 接下来我们会一起来学习防抖和节流函数:
- 我们不仅仅要区分清楚防抖和节流两者的区别,也要明白在实际工作中哪些场景会用到;
- 并且我会带着大家一点点来编写一个自己的防抖和节流的函数,不仅理解原理,也学会自己来编写;
# 1.2.认识防抖debounce函数
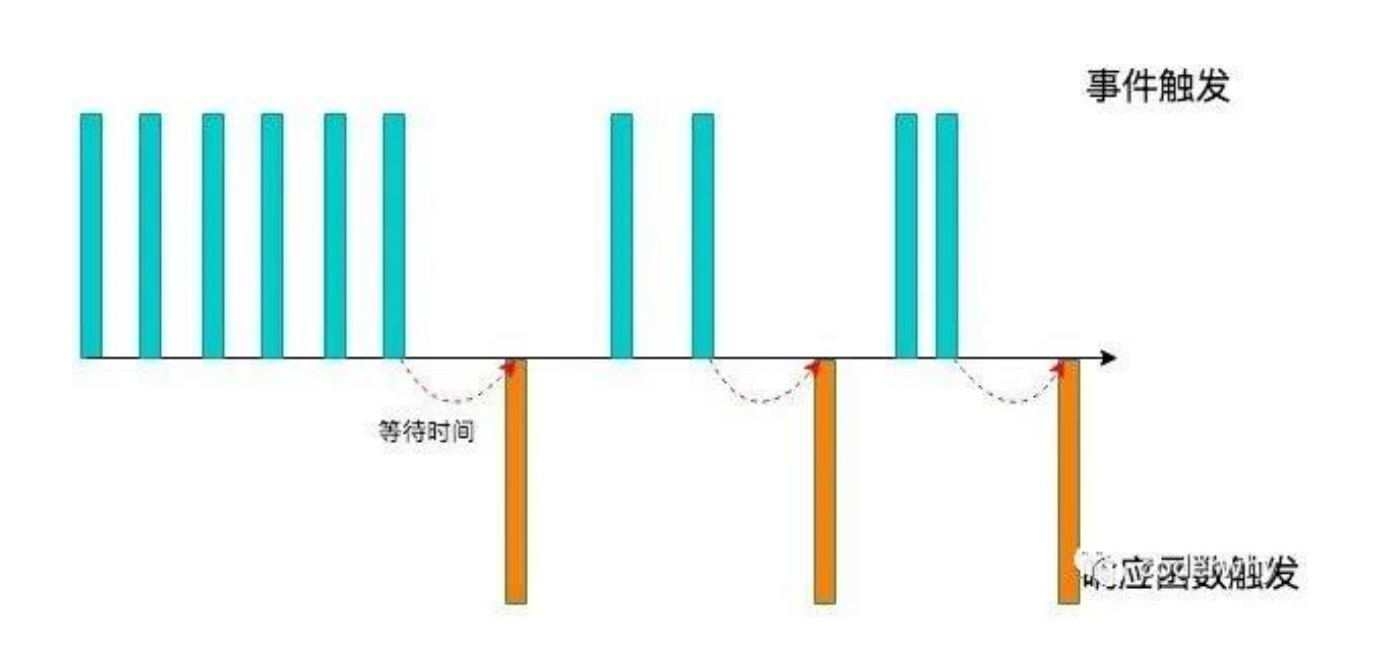
- 我们用一副图来理解一下它的过程:
- 当事件触发时,相应的函数并不会立即触发,而是会等待一定的时间;
- 当事件密集触发时,函数的触发会被频繁的推迟;
- 只有等待了一段时间也没有事件触发,才会真正的执行响应函数;
- 防抖的应用场景很多:
- ➢输入框中频繁的输入内容,搜索或者提交信息;
- ➢频繁的点击按钮,触发某个事件;
- ➢监听浏览器滚动事件,完成某些特定操作;
- ➢用户缩放浏览器的resize事件;
# 1.3.防抖函数的案例
- 我们都遇到过这样的场景,在某个搜索框中输入自己想要搜索的内容:
- 比如想要搜索一个MacBook:
- 当我输入m时,为了更好的用户体验,通常会出现对应的联想内容,这些联想内容通常是保存在服务器的,所以需要一次网络请求;
- 当继续输入ma时,再次发送网络请求;
- 那么macbook一共需要发送7次网络请求;
- 这大大损耗我们整个系统的性能,无论是前端的事件处理,还是对于服务器的压力;
- 但是我们需要这么多次的网络请求吗?
- 不需要,正确的做法应该是在合适的情况下再发送网络请求;
- 比如如果用户快速的输入一个macbook,那么只是发送一次网络请求;
- 比如如果用户是输入一个m想了一会儿,这个时候m确实应该发送一次网络请求;
- 也就是我们应该监听用户在某个时间,比如500ms内,没有再次触发时间时,再发送网络请求;
- 这就是防抖的操作:只有在某个时间内,没有再次触发某个函数时,才真正的调用这个函数;
# 1.4.生活中的例子:防抖
- 比如说有一天我上完课,我说大家有什么问题来问我,我会等待五分钟的时间。
- 如果在五分钟的时间内,没有同学问我问题,那么我就下课了;
- 在此期间,a同学过来问问题,并且帮他解答,解答完后,我会再次等待五分钟的时间看有没有其他同学问问题;
- 如果我等待超过了5分钟,就点击了下课(才真正执行这个时间);
# 1.5.案例准备
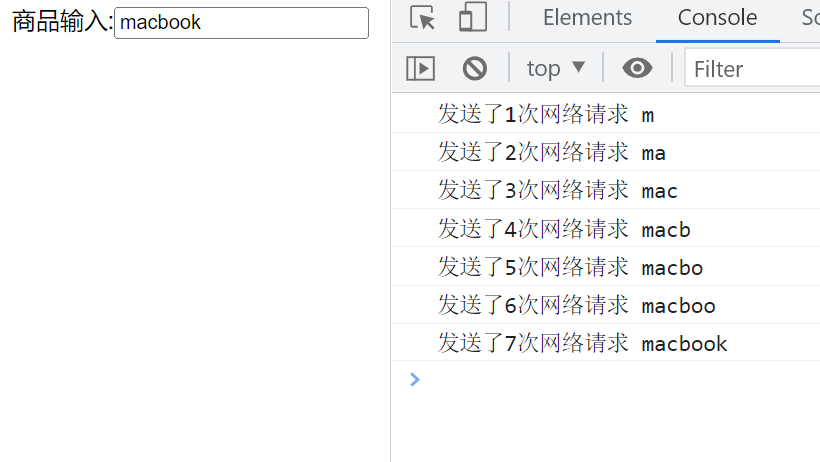
- 我们通过一个搜索框来延迟防抖函数的实现过程:监听input的输入,通过打印模拟网络请求
- 测试发现快速输入一个macbook共发送了7次请求,显然我们需要对它进行防抖操作:
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<script>
let index = 1
const input = document.querySelector('input')
input.oninput = function() {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`,this.value)
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
- 下面我们用一个Underscore库,使用库中已经封装好的防抖函数来解决这个问题;
# 1.6.Underscore库的介绍
- 事实上我们可以通过一些第三方库来实现防抖操作:
- lodash 库
- underscore 库
- 这里使用underscore
- 我们可以理解成lodash是underscore的升级版,它更重量级,功能也更多;
- 但是目前我看到underscore还在维护,lodash已经很久没有更新了;
- Underscore的官网 (opens new window)
- Underscore的安装有很多种方式:
- 下载Underscore,本地引入;
- 通过CDN直接引入;
- 通过包管理工具(npm)管理安装;
- 这里我们直接通过CDN:
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/underscore@1.13.4/underscore-umd-min.js库中防抖函数功能具体用法 (opens new window) - 用Underscore的_.debounce实现防抖
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/underscore@1.13.4/underscore-umd-min.js"></script>
<script>
let index = 1
const input = document.querySelector('input')
//_.debounce(function, wait, [immediate])
input.oninput =_.debounce( function() {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`,this.value)
}, 1000, true)
const debounce = _.debounce(function() {
return 'kobe'
},1000)
console.log(debounce())//undefined
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- 下面我们自己来试着手写一下这个防抖的功能函数吧
# 2、自定义实现防抖函数
# 2.1.我们按照如下思路来实现:
# 2.2.防抖基本功能实现:可以实现防抖效果
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce (fn,delay) {
let timer = null
const _debounce = () => {
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(()=> {
fn()
timer = null
},delay)
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
input.oninput = ykDebounce(function() {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`,this.value)
},1000)
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 2.3.优化一:优化参数和this指向
- ->实现到这里你就知道防抖的核心代码了
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce (fn,delay) {
let timer = null
const _debounce = function(...args) {
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(()=> {
fn.apply(this,args)
timer = null
},delay)
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
input.oninput = ykDebounce(function() {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`,this.value)
},1000)
const _debounce = ykDebounce(function(name,age){
console.log({name:name,age:age})
},3000)
_debounce('lyk',99)
_debounce('lyk',99)
_debounce('lyk',99)
_debounce('lyk',99)
_debounce('lyk',199)
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# 2.4.优化二:优化取消操作(增加取消功能cancel)
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<button>取消</button>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce(fn, delay) {
let timer = null
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
//给防抖函数绑定一个取消函数
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
const debounce = ykDebounce(function () {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`, this.value)
},2000)
input.oninput = debounce
btnEl.onclick = debounce.cancel
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 2.5.优化三:优化立即执行效果(第一次立即执行immediate)
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<button>取消</button>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
let timer = null
let immediateFlag = true
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
console.log('触发了事件')
if (!immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
if (immediate && immediateFlag) {
fn.apply(this, args)
immediateFlag = false
}
if (immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('时间到了------------')
timer = null
immediateFlag = true
}, delay)
}
}
//给防抖函数绑定一个取消函数
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
const debounce = ykDebounce(function () {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`, this.value)
}, 600, true)
input.oninput = debounce
btnEl.onclick = debounce.cancel
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# 2.6.优化四:优化返回值(ES5回调函数方案)
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<button>取消</button>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce(fn, delay, callBack, immediate = false) {
let timer = null
let immediateFlag = true
const _debounce = function (...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
console.log('触发了事件')
if (!immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
callBack(result)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
if (immediate && immediateFlag) {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
callBack(result)
immediateFlag = false
}
if (immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('时间到了------------')
timer = null
immediateFlag = true
}, delay)
}
}
//给防抖函数绑定一个取消函数
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
const debounce = ykDebounce(function () {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`, this.value)
return this.value
}, 600, function(res){
console.log(`拿到返回值:`,res)
},false)
input.oninput = debounce
btnEl.onclick = debounce.cancel
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 2.7.优化四:优化返回值(Promise方案)
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<button>取消</button>
<script>
let index = 1
function ykDebounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
let timer = null
let immediateFlag = true
const _debounce = function (...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
console.log('触发了事件')
if (!immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(result)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
//立即执行效果
if (immediate && immediateFlag) {
const result = fn.apply(this, args)
resolve(result)
immediateFlag = false
}
if (immediate) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('时间到了------------')
timer = null
immediateFlag = true
}, delay)
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
//给防抖函数绑定一个取消函数
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
console.log('取消操作')
}
return _debounce
}
const input = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
const debounce = ykDebounce(function () {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`, this.value)
return '我是返回值'
}, 600, false)
input.oninput = debounce
const debounce1 = ykDebounce(function (name, age) {
return { name: name, age: age }
}, 1000)
debounce1('kobe', 39).then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
btnEl.onclick = debounce1.cancel
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
# 3、节流throttle函数的深入学习
# 3.1.认识节流throttle函数
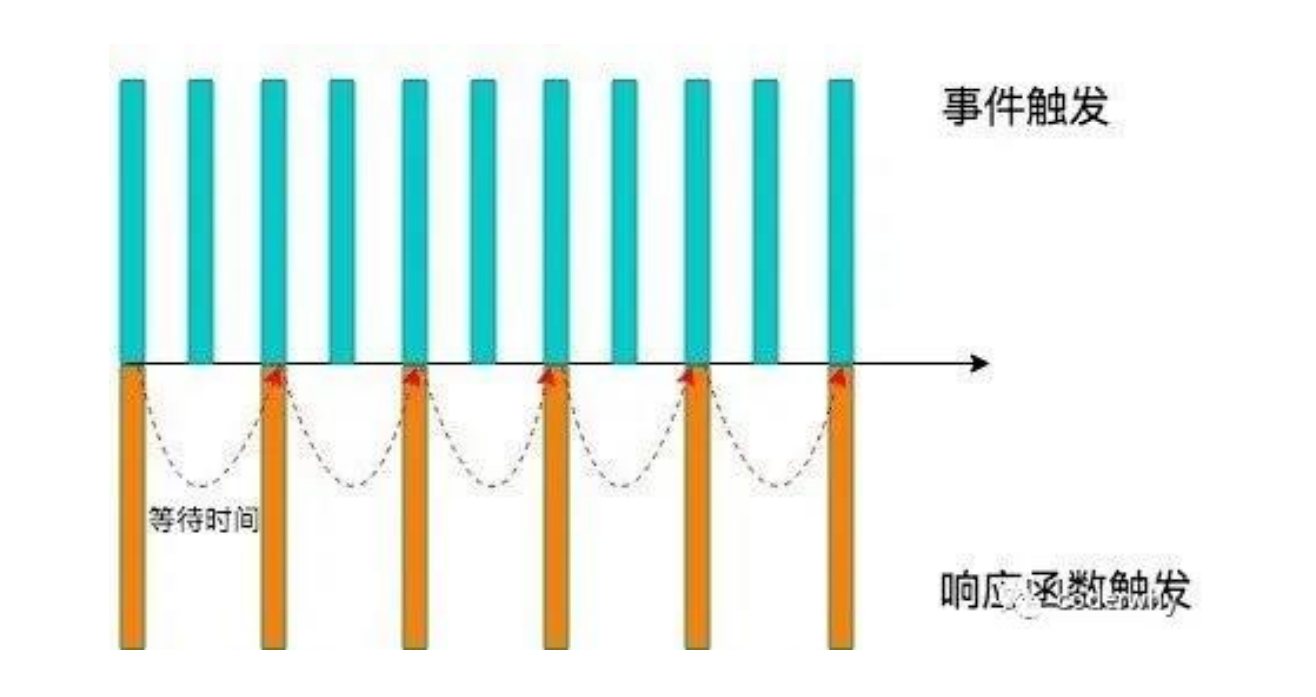
我们用一副图来理解一下节流的过程
当事件触发时,会执行这个事件的响应函数;
如果这个事件会被频繁触发,那么节流函数会按照一定的频率来执行函数;
不管在这个中间有多少次触发这个事件,执行函数的频繁总是固定的;
- 节流的应用场景:
- ➢ 监听页面的滚动事件;
- ➢ 鼠标移动事件;
- ➢ 用户频繁点击按钮操作;
- ➢ 游戏中的一些设计;
# 3.2.节流函数的应用场景
- 很多人都玩过类似于飞机大战的游戏
- 在飞机大战的游戏中,我们按下空格会发射一个子弹:
- 很多飞机大战的游戏中会有这样的设定,即使按下的频率非常快,子弹也会保持一定的频率来发射;
- 比如1秒钟只能发射一次,即使用户在这1秒钟按下了10次,子弹会保持发射一颗的频率来发射;
- 但是事件是触发了10次的,响应的函数只触发了一次;

# 3.3.生活中的例子:节流
- 比如说有一天我上完课,我说大家有什么问题来问我,但是在一个5分钟之内,不管有多少同学来问问题,我只会解答一个问题;
- 如果在解答完一个问题后,5分钟之后还没有同学问问题,那么就下课
# 3.4.Underscore库使用节流功能
- 这里我们直接通过CDN:
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/underscore@1.13.4/underscore-umd-min.js库中j节流函数功能具体用法 (opens new window) - 用Underscore的_.debounce实现防抖
<label for="shop">
商品输入:<input type="text" id="shop">
</label>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/underscore@1.13.4/underscore-umd-min.js"></script>
<script>
let index = 1
const input = document.querySelector('input')
// _.throttle(function, wait, [options])
//options参数:如果您想禁用前沿调用,请传递{leading: false},如果您想禁用后沿执行,请传递{trailing: false}。默认:它两值都为true
input.oninput = _.throttle(function () {
console.log(`发送了${index++}次网络请求`, this.value)
}, 1000,{leading:true,trailing:false})
const throttle = _.throttle(function () {
return 'lyk'
}, 3000)
console.log(throttle())//lyk
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 下面我们试着手写一下节流功能函数吧
# 4、自定义实现节流函数
# 4.1.我们按照如下思路来实现:
# 4.2.节流函数的基本实现:
可以实现节流效果(并优化参数和this指向 )
(实现到这里你就知道节流的核心代码了)
商品输入:<input type="text">
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector('input')
let index = 1
function ykThrottle(fn, interval) {
let startTime = 0
return function _throttle(...args) {
// 1.获取当前时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 2.计算需要等待的时间执行函数
const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime)
if (waitTime <= 0) {
fn.apply(this,args)
startTime = nowTime
}
}
}
const throttle = ykThrottle(function () {
console.log('发送网络请求', index++)
},1000)
inputEl.oninput = throttle
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 4.3.优化一:节流的立即执行效果(第一次立即执行)控制
商品输入:<input type="text">
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector('input')
let index = 1
function ykThrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true } = {}) {
let startTime = 0
return function _throttle(...args) {
// 1.获取当前时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 对立即执行进行控制leading
if (!leading && startTime===0) {
startTime = nowTime
}
// 2.计算需要等待的时间执行函数
const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime)
if (waitTime <= 0) {
fn.apply(this, args)
startTime = nowTime
}
}
}
const throttle = ykThrottle(function () {
console.log('发送网络请求', index++)
}, 1000, { leading: false })
inputEl.oninput = throttle
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 4.4.优化二:节流最后一次也可以执行(尾部控制)
商品输入:<input type="text">
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector('input')
let index = 1
function ykThrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = true } = {}) {
let startTime = 0
let timer = null
return function _throttle(...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 1.获取当前时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 对立即执行进行控制leading
if (!leading && startTime === 0) {
startTime = nowTime
}
// 2.计算需要等待的时间执行函数
const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime)
if (waitTime <= 0) {
console.log('正常调用')
fn.apply(this, args)
startTime = nowTime
// return
}
//3.对最后一次执行进行控制(尾部控制)trailing
if (waitTime > 0 && trailing) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timer')
fn.apply(this, args)
startTime = nowTime
timer = null
}, waitTime)
}
}
}
const throttle = ykThrottle(function () {
console.log('发送网络请求', index++)
}, 1000, { leading: false, trailing: true })
inputEl.oninput = throttle
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 4.5.优化三:优化添加取消功能cancel()
商品输入:<input type="text">
<button>取消节流阀</button>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
let index = 1
function ykThrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = true } = {}) {
let startTime = 0
let timer = null
function _throttle(...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 1.获取当前时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 对立即执行进行控制leading
if (!leading && startTime === 0) {
startTime = nowTime
}
// 2.计算需要等待的时间执行函数
const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime)
if (waitTime <= 0) {
console.log('正常调用')
fn.apply(this, args)
startTime = nowTime
return
}
//3.对最后一次执行进行控制(尾部控制)trailing
if (trailing) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timer')
fn.apply(this, args)
startTime = Date.now()
timer = null
}, waitTime)
}
}
//4.添加取消功能cancel()
_throttle.cancel = function() {
startTime = 0
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
}
return _throttle
}
const throttle = ykThrottle(function () {
console.log('发送网络请求', index++)
}, 3000, { leading: true, trailing: true })
inputEl.oninput = throttle
btnEl.addEventListener('click',function() {
console.log('取消了节流阀')
throttle.cancel()
})
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# 4.6.优化四:优化返回值问题(Promise)
商品输入:<input type="text">
<button>取消节流阀</button>
<script>
const inputEl = document.querySelector('input')
const btnEl = document.querySelector('button')
let index = 1
function ykThrottle(fn, interval, { leading = true, trailing = true } = {}) {
let startTime = 0
let timer = null
function _throttle(...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
// 1.获取当前时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime()
// 对立即执行进行控制leading
if (!leading && startTime === 0) {
startTime = nowTime
}
// 2.计算需要等待的时间执行函数
const waitTime = interval - (nowTime - startTime)
if (waitTime <= 0) {
console.log('正常调用')
resolve(fn.apply(this, args))
startTime = nowTime
return
}
//3.对最后一次执行进行控制(尾部控制)trailing
if (trailing) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timer')
resolve(fn.apply(this, args))
startTime = Date.now()
timer = null
}, waitTime)
}
} catch (err) {
reject(err)
}
})
}
//4.添加取消功能cancel()
_throttle.cancel = function () {
startTime = 0
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
}
return _throttle
}
const throttle = ykThrottle(function (name, age) {
console.log('发送网络请求', index++)
return { name, age }
}, 3000, { leading: true, trailing: true })
inputEl.oninput = throttle
btnEl.addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('取消了节流阀')
throttle.cancel()
})
throttle('kobe', 39).then(res => {
console.log('拿到返回值:', res)
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
throttle('kobe', 39).then(res => {
console.log('拿到返回值:', res)
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
throttle('kobe', 39).then(res => {
console.log('拿到返回值:', res)
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error)
})
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
# 5、自定义深拷贝函数
- 前面我们已经学习了对象相互赋值的一些关系,分别包括:
- 引入的赋值:指向同一个对象,相互之间会影响;
- 对象的浅拷贝:只是浅层的拷贝,内部引入对象时,依然会相互影响;
- 对象的深拷贝:两个对象不再有任何关系,不会相互影响;
- 前面我们已经可以通过一种方法来实现深拷贝了:
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(value))- 这种深拷贝的方式其实对于函数、Symbol等是无法处理的;
- 并且如果存在对象的循环引用,也会报错的;
- 自定义深拷贝函数:
- 自定义深拷贝的基本功能;
- 对Symbol的key进行处理;
- 其他数据类型的值进程处理:对象,数组、函数、Symbol、Set、Map;
- 对循环引用的处理;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 一:封装一个函数判断 是否是引用类型
function isObject(value) {
const type = typeof value
return value !== null && (type === 'object' || type === 'function')
}
// 二:自定义深拷贝的全部功能;
function deepCopy(originValue, map = new WeakMap) {
// 0.如果值是Symbol的类型
if (typeof originValue === "symbol") {
return Symbol(originValue.description)
}
//1.如果是原始数据类型 或者是函数function类型, 不需要进行深拷贝, 直接返回
if (!isObject(originValue) || typeof originValue === 'function') {
return originValue
}
//3.如果是set类型 则对Set类型进行处理
if (originValue instanceof Set) {
let newSet = new Set()
for (const setItem of originValue) {
newSet.add(deepCopy(setItem))
}
return newSet
}
//5.循环引用解决方案:WeakMap
if (map.has(originValue)) {
return map.get(originValue)
}
//2.如果是对象类型,才需要创建新的对象
const newObj = Array.isArray(originValue) ? [] : {}
map.set(originValue, newObj)
console.log(map)
for (const key in originValue) {
newObj[key] = deepCopy(originValue[key], map)
}
//4. 单独遍历Symbol,以为属性为Symbol类型,通过枚举是枚举不出来的;
//只能通过Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(obj)方法来获取,对象属性为Symbol类型 的值
//下面对属性为Symbol类型的特殊处理
const symbolKeys = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(originValue)
for (const symbolKey of symbolKeys) {
newObj[Symbol(symbolKey.description)] = deepCopy(originValue[symbolKey], map)
}
return newObj
}
//三:用来测试自定义深拷贝工具函数
const friends = ['curry', 'james']//测试set类型中的深拷贝
const s1 = Symbol('s1')
const obj = {
name: 'kobe',
address: {
city: '上海',
detail: '浦东新区'
},
friends: ['curry', 'james'],
running() {
console.log(this.friends[0])
},
set: new Set(['nba', 'cba', friends]),
[s1]: 'ncaaya'
}
obj.info = obj //循环引用
const newObj = deepCopy(obj)
newObj.address.city = '广州'
newObj.set.delete('nba')
newObj.friends[0] = 'lyk'
friends[0] = 'rose'//测试set类型中的深拷贝
console.log('obj:', obj)
console.log('newObj:', newObj)
obj.running()
newObj.running()
console.log(obj[s1] === newObj[s1])
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
# 6、自定义事件总线
- 自定义事件总线属于一种观察者模式,其中包括三个角色:
- 发布者(Publisher):发出事件(Event);
- 订阅者(Subscriber):订阅事件(Event),并且会进行响应(Handler);
- 事件总线(EventBus):无论是发布者还是订阅者都是通过事件总线作为中台的;
- 当然我们可以选择一些第三方的库:
- Vue2默认是带有事件总线的功能;
- Vue3中推荐一些第三方库,比如mitt;
- 当然我们也可以实现自己的事件总线:
- 事件的监听方法on;
- 事件的发射方法emit;
- 事件的取消监听off;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button class="nav-btn">nav button</button>
<script>
// 类EventBus -> 事件总线对象
class ykEventBus {
constructor() {
this.eventMap = {}// {navclick:[fn]}
}
on(eventName, eventFn) {//监听方法
let eventFns = this.eventMap[eventName]
if (!eventFns) {
eventFns = []
this.eventMap[eventName] = eventFns
}
eventFns.push(eventFn)
}
emit(eventName, ...args) {//发出事件
let eventFns = this.eventMap[eventName]
if (!eventFns) return
eventFns.forEach(fn => {
fn(...args)
})
}
off(eventName, eventFn) {
let eventFns = this.eventMap[eventName]
if (!eventFns) return
for (let i = 0; i < eventFns.length; i++) {
const fn = eventFns[i]
if (fn === eventFn) {
eventFns.splice(i, 1)
break
}
}
// 如果eventFns已经清空了
if (eventFns.length === 0) {
delete this.eventMap[eventName]
}
}
}
// 使用过程
const eventBus = new ykEventBus()
// aside.vue组件中监听事件
const click1 = (name, age, height) => {
console.log("navclick listener 01", name, age, height)
}
const click2 = () => {
console.log("navclick listener 02")
}
eventBus.on("navclick", click1)
eventBus.on("navclick", click2)
setTimeout(() => {
eventBus.off("navclick", click2)
}, 5000);
eventBus.on("asideclick", () => {
console.log("asideclick listener")
})
// nav.vue
const navBtnEl = document.querySelector(".nav-btn")
navBtnEl.onclick = function() {
console.log("自己监听到")
eventBus.emit("navclick", "kobe", 39, 1.98)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95

